
What Does Evapotranspiration Mean?

Table of Contents
As much as 99% of the water plants take up in the field, particularly in arid regions, is lost through evapotranspiration (ET). The plants rely on less than 1% of the water to produce plant tissues. Farmers, environmentalists, and nations are currently at the forefront in tracking evapotranspiration since it’s helpful for developing highly efficient ways to mitigate the adverse impact of global warming and climate change.
What is Evapotranspiration?

Elephant dies after evapotranspiration PixaBay
The term ‘evapotranspiration’ refers to the loss of water from the soil and wet vegetation to the atmosphere through evaporation and from plant tissues through transpiration.
Evaporation (E)
It involves the transformation of liquid water to water vapor. Once the conversion occurs, the soil and leaves of plants dry up, hindering photosynthesis from taking place as required.
Transpiration (T)
Transpiration refers to the process that causes plants to lose water through their stomata. These are tiny pores in the leaves of plants that allow for gas exchange. During the day, green plants take in carbon dioxide and release Oxygen. They do the reverse at night. Hot weather or the sun transforms water in plant tissues into vapor. After the conversion, the water escapes through these openings, especially during the day.
The figure below illustrates how ET occurs. It can help you see why climate change threatens many ecosystems in the world today.

The evapotranspiration process Source
How Does Evapotranspiration Impact Plant Growth?
In landscapes where irrigated crops provide complete ground cover, a significant amount of water loss happens through transpiration. The high losses are directly linked to plant productivity and growth.
When plants receive adequate water from the ground, the stomata stay widely open. This increases the transpiration rate. However, when plants can’t access adequate water, these openings close partially to limit transpiration.
Unfortunately, the closure of the stomata, especially during the day, can hinder plants from taking in the required amount of carbon dioxide, which they rely on for photosynthesis. So, one must understand the link between photosynthesis and the closing of the stomata during the day. In other words, your knowledge of evapotranspiration in your area could help you understand your plants’ water needs. Farmers use this to determine water application efficiency. If an adequate amount of the supplied water is stored in the crop root zone, the application efficiency is high enough.
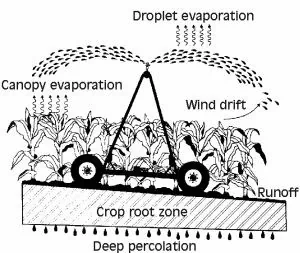
Crop root zone Source
The most critical parameters that experts use to determine water application efficiency are:
- Water distribution characteristics
- Soil conditions
- Weather conditions
- System management
It’s critical to note that the world currently relies on about 70%-and-75% of fresh water for irrigation. This shows that the management of freshwater requires more attention today than ever.
The current irrigation efficiency is below the recommended 50%-to-60%. In many instances, it falls between 20% and 30%. This underscores the widespread understanding that the globe is yet to use the Earth’s irrigation potential.
Is Evapotranspiration Important?
From the above analysis, some people might think evapotranspiration is part of the cause of the world’s current environmental problems. That’s not the case. Poor management of our ecosystem is responsible for the water stress the world is experiencing.
Evapotranspiration allows the continuous circulation of water between the oceans, sky, and land. This process is responsible for about 15% of the water vapor in the atmosphere. Without this, clouds can’t form. So, evapotranspiration is fundamental to the availability of water on the Earth.

Clouds forming PixaBay
Water Scarcity Causes and Contributing Factors
Evapotranspiration is essential for the existence of life on the planet Earth. However, water scarcity causes and contributes factors that could hinder it from doing this. For that matter, it’s necessary to identify the threats and find ways to minimize their impact.
Some of the factors that have led to overdependence on irrigation and extreme water stress across the world are:
Increasing population
Studies have shown that a quarter of the world’s pollution experiences extreme water stress due to population growth. About five decades ago, when the world’s population was less than half of the current number of people, almost everyone regarded water as an infinite resource. The current world population is close to eight billion. The United Nations projects that it will hit the 9.9-billion mark by 2050.
Today, more people are wealthy and consume lots of calories and eat more meat. So, we require more water than before to prepare food, irrigate our lands, and more. With the UN projection, the situation is likely to worsen in the coming days if we hesitate to take the required action.
Solution: All individuals, cities, nations, and organizations should increase water conservation and recycling. This should be done while considering the impact of various environmental and social variables, such as climate change.
Climate Change
Climate change could be one of the leading reasons evapotranspiration might not serve its intended purpose in the coming days. The close connection between the hydrological cycle and climate could worsen the situation.

Hydrological cycle cause bad climate PixaBay
Global warming will increase evapotranspiration. This shows that the world will most likely experience increased precipitation. Moreover, due to the changes in the underlying forces that cause the hydrological cycle, regional variations in rainfall patterns will most likely characterize the future. Besides, as already witnessed in many parts of the world, floods and droughts might become more prevalent in various geographical locations at different, unpredictable times. Furthermore, the increase in evapotranspiration will most likely lead to significant dramatic changes in snowmelt and snowfall, especially in mountainous regions. Other possible impacts of the increased evapotranspiration include:
- Increased eutrophication: Water bodies will progressively get enriched with nutrients and minerals
- Increased demand for farm irrigation
- Altered future patterns of water availability and use
- Increased receding glaciers
Solution: Industries, cities, and nations find better ways to use and recycle water. Farmers increase productivity to meet the increasing demand for food.
Long-Term Impacts of the Increasing Evapotranspiration
Since water supports human life, there are numerous potential manifestations of increasing evapotranspiration. The most common ones are:
- Food security in several parts of the world
- Inadequate access to drinking water
- Water pollution due to insufficient access to sanitation
- Excessive use of groundwater
- Diminished agricultural yields
- Water pollution leading to harming of biodiversity
- Conflict in different parts of the world over scarce water resources
By conserving the environment and avoiding human activities like burning fossil fuels, it’s possible to stop or minimize global warming and climate change.
Why Evapotranspiration Irrigation Systems Are Necessary Today?
Due to the current climate challenges, farmers need an irrigation system that mitigates the water stress problem. The best method should be able to help you to:
- Accurately determine the amount of water that your plants and the surrounding soil take in at any time
- Determine the amount of water various categories of landscapes require
- Reduce plant diseases and other related conditions
- Increase the lifespan of your farm’s asphalt and paved surfaces
- Minimizes soil consolidation
- Reduce water runoff
How to Calculate Evapotranspiration?
To calculate EV accurately, you need to understand the factors that impact it first. Here are the major atmospheric factors:
Temperature
As the temperature rises, the rate of transpiration and evaporation goes up as well. This trend is more prevalent during the growing season when stronger sunlight and warmer air masses make the air warmer. Global warming can also cause this. Warmer temperatures stimulate the stomata to open, leading to increased loss of water to the atmosphere.
Relative Humidity
The transpiration rate falls as the relative humidity around the plants rise. Water evaporates with much more ease in a dyer air than a saturated one.
Wind and Air Movement
Increased flow of wind around plants enhances the rate of transpiration. The movement replaces the more saturated air near the leaves with much drier air, escalating the ET rate.
Soil-Moisture Availability
Plants typically begin to prematurely age when they can’t access adequate water. This process helps them to transpire less water.
Plant Type
Some plants transpire at a higher rate than others. For example, plants that do well in arid and semi-arid areas conserve water.
Every site has varied water needs, and the requirements change from time to time. This explains why many irrigation solutions that attempt to define microclimates and set watering schedules fail to yield the desired results. They use remote weather stations. Others rely on stations with limited zip codes or sensors.
Here are some common ways of calculating evapotranspiration that you can consider:
-
Averaging evapotranspiration from adjacent weather stations: This can produce accurate results. However, since microclimates can differ significantly, it isn’t a perfect remedy.
-
Blaney-Criddle: This method tends to give accurate results in areas with lower humidity.
-
Hargreaves: It’s another popular method. Hargreaves uses one sensor. However, it can produce results that are up to 60% different from other methods.
-
ASCE Standardized Penman-Monteith: As you can see, you might need to use various methods to calculate ET accurately. The American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE) conducted in-depth research to find a single way that people can use to estimate ET. They resolved that the ASCE Standardized Penman-Monteith is the most efficient method for doing this.
ET calculations take into account so many factors. Many people consider this method problematic on this basis.
Concluding on What Does Evapotranspiration Mean
Now you understand how evapotranspiration matters to the planet Earth. It helps us understand the impact of climate change and global warming. Unfortunately, calculating EV can be problematic to many people. So, other than developing advanced, simple ET-calculation methods, humans need to preserve the environment to minimize the negative impacts of various environmental variables like climate change.